Unlocking the Mysteries of 831b: Exploring its Hidden Potential
The world of insurance is a vast and intricate web, with various options available to individuals and businesses alike. One particular avenue that has caught the attention of many is the elusive 831b. Housed within the labyrinthine depths of the IRS tax code, this captivating provision offers an intriguing opportunity for those seeking alternative risk management strategies.
At first glance, the mention of "831b" may seem unfamiliar and enigmatic, but fear not, as we embark on a journey to uncover the secrets behind this captivating concept. By delving into the realm of captive insurance, we will shed light on why microcaptives, as they are commonly known, have become a topic of interest for savvy entrepreneurs and forward-thinking investors.
Imagine a scenario where a business can protect itself against unforeseen risks, while also enjoying potential tax benefits. This is the promise that 831b holds, enabling businesses to form their own captive insurance companies, tailored to their specific needs. As we unravel the intricacies of this provision, we will uncover the hidden potential that lies within it, unlocking insights that will be valuable for individuals and organizations seeking more control over their risk management strategies.
Join us as we embark on a fascinating journey through the inner workings of 831b. Together, we will delve into the depths of captive insurance and explore the limitless possibilities that arise from understanding this lesser-known aspect of the IRS tax code. Prepare to be enlightened and empowered as we demystify the intricacies of 831b and reveal the hidden potential that awaits those who dare to explore.
Understanding 831b: An Introduction
Captive Insurance
An individual or a business looking for ways to manage and mitigate risks while potentially gaining tax advantages may stumble upon an intriguing option known as 831b. This particular concept is closely linked to captive insurance, offering an alternative to traditional insurance methods. With the help of the IRS 831b tax code, this approach allows businesses to create their own microcaptive insurance companies, tailor-made to their specific requirements.
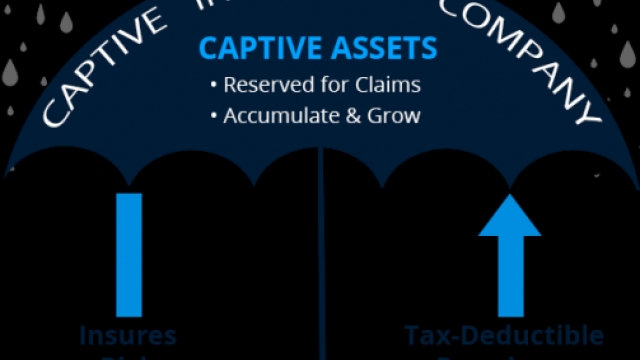
Captive insurance refers to a method where a business forms its own insurance company to provide coverage for risks associated with its operations. This enables the business to have more control over its insurance policies, claims management, and potential financial benefits. The micrcaptive insurance concept takes this idea even further, being a specific type of captive insurance company that falls under the guidelines of the IRS 831b tax code.
The IRS 831b tax code was implemented to encourage small- to medium-sized businesses to form their own captive insurance companies. By doing so, these businesses have the opportunity to potentially reduce their overall tax liability. The tax code outlines specific requirements and limits for the microcaptive insurance companies, helping to define their functioning and eligibility.
Understanding 831b, captive insurance, and the IRS 831b tax code is crucial for those interested in exploring the hidden potential of this approach. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the workings of 831b, its benefits, and considerations to keep in mind when contemplating whether it is a suitable path for your risk management and tax planning needs.
Exploring the Benefits of Captive Insurance
Captive insurance, specifically under the IRS 831(b) tax code, offers a range of benefits for businesses. This alternative risk management strategy allows companies to create their own insurance company, known as a microcaptive, to provide coverage for their specific needs. By exploring the potential of 831(b) captive insurance, businesses can tap into hidden opportunities to enhance their risk management approaches.
One significant advantage of captive insurance is the opportunity for cost savings. Traditional insurance premiums can be substantial, and businesses often find themselves paying for coverage they don’t necessarily need. With an 831(b) captive, companies can tailor their insurance program to align precisely with their unique risks. By retaining more risk and self-insuring, businesses can potentially reduce their overall insurance costs and allocate resources more efficiently.
Furthermore, captive insurance allows businesses to gain greater control over their risk management strategies. By operating their insurance company, companies have the flexibility to customize coverage, set underwriting guidelines, and even gain access to additional risk management tools. This increased control enables businesses to align their risk management approaches with their overall business objectives, ensuring that their insurance program compliments their broader strategies.
Another benefit of captive insurance is the potential for improved cash flow. With a traditional insurance program, premiums are paid to an external insurer, and claims are paid out when necessary. However, with an 831(b) captive, businesses can retain their premiums within their own insurance company. This retention enables them to invest the funds and potentially generate additional income, providing a financial advantage over time.

In conclusion, captive insurance, specifically under the IRS 831(b) tax code, presents businesses with a range of benefits. From cost savings and increased control to improved cash flow, exploring the potential of captive insurance can unlock hidden opportunities for businesses seeking a more customized and efficient risk management approach.
Navigating the IRS 831b Tax Code
The IRS 831b tax code refers to a specific provision that allows small insurance companies, known as microcaptives, to elect alternative tax treatment. This unique provision, often misunderstood, can offer significant benefits for businesses seeking to manage their risks effectively and potentially reduce their overall tax liability.
Captive insurance companies, including those falling under the 831b category, are an alternative risk management tool used by businesses to self-insure certain risks. By forming their own insurance company, businesses can gain greater control over their insurance program and tailor it to their specific needs. This approach can be particularly advantageous for businesses facing limited options or high costs in traditional insurance markets.
Under the IRS 831b tax code, a microcaptive is an insurance company that satisfies certain ownership and risk criteria. To qualify, the insurance company must have annual premiums of $2.3 million or less. Additionally, at least 70% of these premiums should come from related entities, meaning the insured risks are affiliated with the business owners or their companies.
By electing to be taxed under the 831b tax code, qualifying microcaptives can enjoy several benefits. For instance, the insurance company’s underwriting profits are tax-exempt, meaning they are not subject to federal income tax. This exemption allows the microcaptive to accumulate funds for future claim payments, investments, and operational expenses on a tax-deferred basis.
Navigating the IRS 831b tax code requires a thorough understanding of the requirements and implications associated with electing this alternative tax treatment. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses exploring the possibilities of forming a microcaptive insurance company to consult with knowledgeable tax advisors and legal professionals to ensure compliance with all IRS regulations.